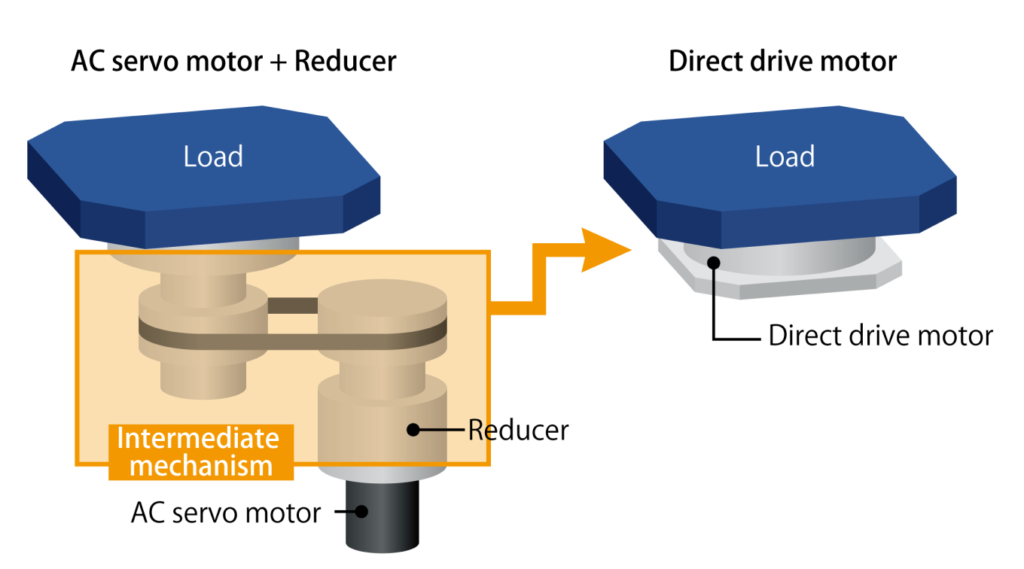
What is a direct drive motor?
The conventional AC servo motor is generally a high-revolution, low-torque motor. In order for this motor to provide high torque, an intermediate mechanism consisting of such components as gears and belts is necessary. This makes the mechanism complex, leading to increased mechanical loss and lower accuracy due to backlash. As a result, the motor requires frequent maintenance.
By contrast, the direct drive motor connects directly to the workpiece without the need for an intermediate mechanism consisting of speed reducers, belts, etc. This makes its power transmission system more rigid and enables backlash-less, high-speed accurate driving. What’s more, the motor saves space and generates quiet drive power.
Structure of the direct drive motor
The direct drive motor mainly consists of four units – stator, rotor, bearing, and rotation position detection sensor (encoder).
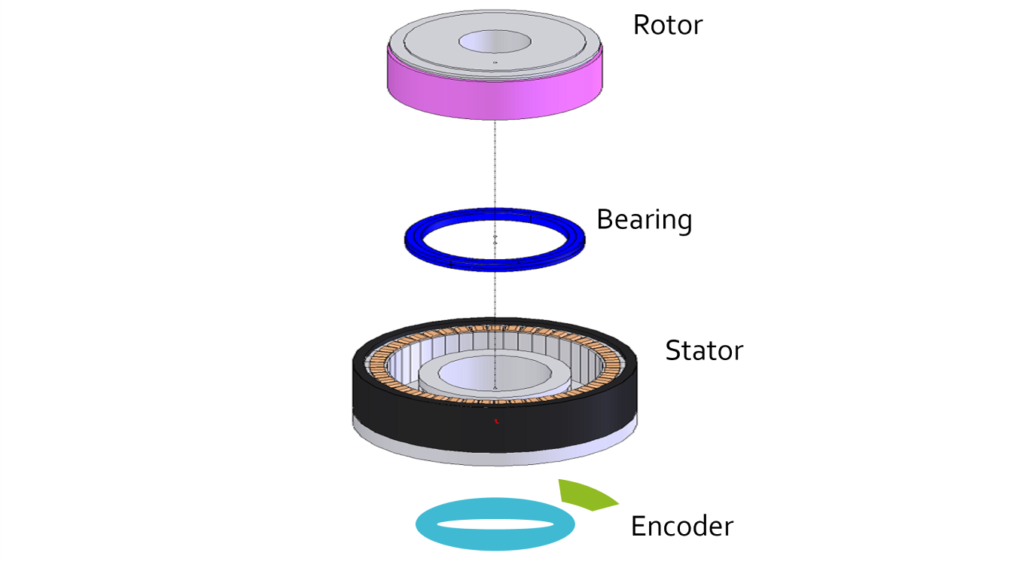
Cross roller bearings are often used. A single bearing can take radial loads, axial loads, and moment loads. These bearings make the motor thinner and much more rigid, compared to when double-row angular ball bearings are used. Moreover, since its structure allows the bearing space to be adjusted, precompression can also be applied, thus providing highly accurate rotation.
In addition, when used with a high-resolution encoder, the motor enables high-accuracy control. When compared to the typical AC servo motor having 8 to 12 motor poles, the direct drive motor features a multi-pole structure with 20 motor poles or more. For larger direct drive motors, the number of motor poles is more than 100. They achieve low torque ripple and large torque.
Features of the direct drive motor and benefits of its introduction
1 | Space-saving
The speed reducer that generates large motor is structurally large and requires a lot of space. With the direct drive motor that needs no speed reducer, by contrast, the entire drive system can be compact and space-saving.
2 | Maintainability
In the case of the AC servo motor with a speed reducer, as the gear sliding part of the speed reducer wears out, the motor needs to be disassembled and cleaned to remove metal powder, degraded grease, and other foreign matter and then reassembled and adjusted. The direct drive motor in principle requires no maintenance because it has a simple structure with no gear sliding part. Moreover, since the motor has no speed reduction mechanism, quick acceleration or deceleration does not cause it to fail, break, or otherwise become damaged.
3 | High response
Thanks to the low-inertia rotation part and the drive system with increased rigidity, the servo control characteristics are directly reflected, making it possible to improve the machine performance.
Video of the high-speed, high-response operation (high-speed handler)
4 | Highly accurate speed control
Since the direct drive motor needs no speed reducer, it has no backlash and many motor poles with little variation in the output torque, thus offering high speed stability. Our direct drive motor τDISC boasts superb speed stability even at low speed. Its speed stability is high enough that the speed variation is ±0.1% (at no load) when the rotation speed is 2 rpm.
Application use cases
Use case 1 | High-speed index mechanism: Test handler
A test handler used to inspect electronic parts has jigs on its disk table, and an index motion is performed with an electronic part put on each jig. The respective task is carried out at each station. An application like this requires high-accuracy, high-response motor to reduce the takt time.
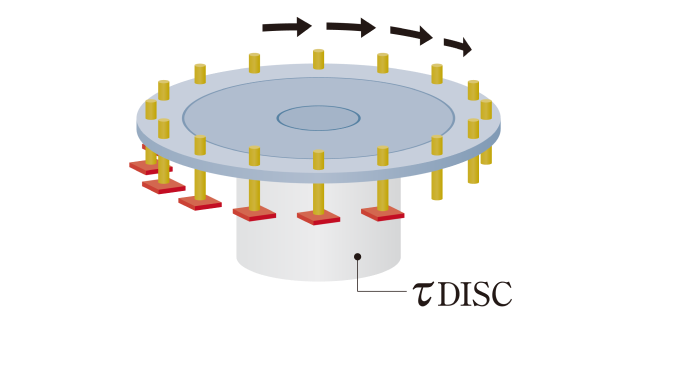
Use case 2 | Alignment of large panels
Since high-accuracy machining is performed at a specific position of the workpiece, accurate positioning and high rigidity are required.
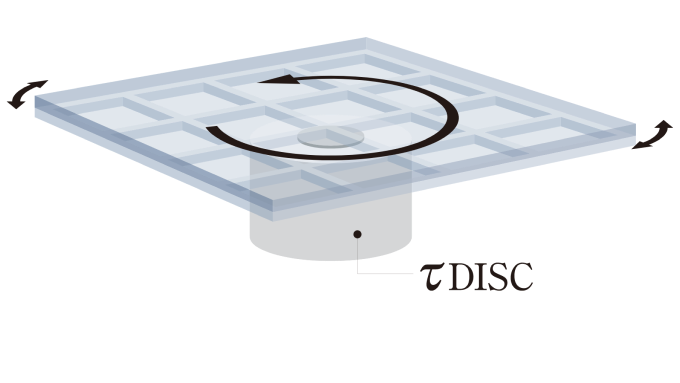
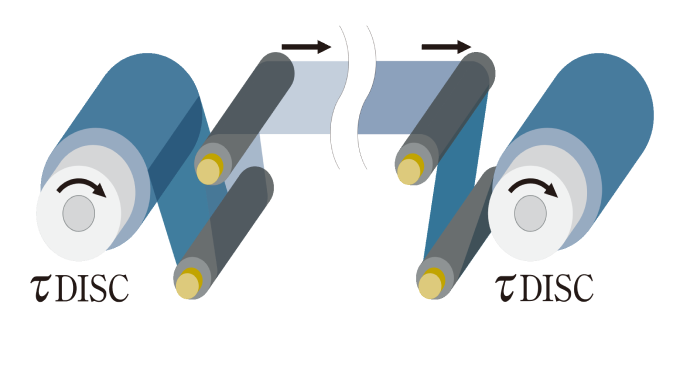
Use case 3 | Winding and unwinding system
This is used for such purposes as to coat a film and known as the roll-to-roll system. While the system has high processing capacity, the feed accuracy is directly related to uneven coating and other processing problems. So, high speed stability is required.
Use case 4 | Steering wheel simulator
Taking advantage of its low torque ripple characteristic, the direct drive motor is used in some cases as a steering wheel simulator that faithfully and naturally represents the response from the road during autonomous driving as the steering torque. Rather than being a mere drive source, the motor is increasingly used for those products that directly impact the equipment performance in areas concerning human sensory evaluations that are difficult to quantify.
Industries where direct drive motors are widely used
Semiconductor and electronic parts industries
Wafer dicing machines, mounters, test handlers, wafer transport machines, wafer chamfering machines, grinders, inspection machines, etc.
Automobile industry
Torque testers, durability testers, steering testers, parts processing machines, transport machines, etc.
FPD industry
Bonding machines, scribers, inspection machines, laser beam machines, etc.
Converting and printer industries
Coating machines, stretching machines, roll coating machines, winding and unwinding mechanisms, laminating machines, PE printers, screen printers, rotary printing presses, etc.
Food-related equipment industry
Capping machines, food transport machines, filling machines, etc.


















